Jim Chrisinger: When elected officials act in bad faith, they poison the well of democracy in many ways. -promoted by Laura Belin
We now know that democracy is more fragile than we thought; democracy requires more than laws and institutions. For example, elected officials need to speak and act in good faith.
Acting in good faith may not seem like the most important thing right now. What makes bad faith so bad?
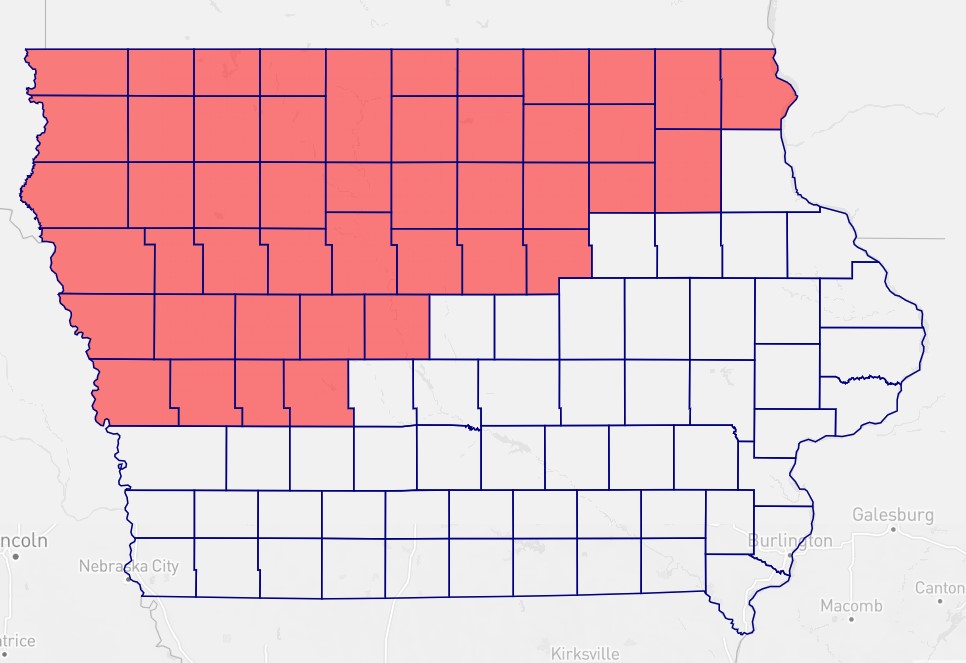
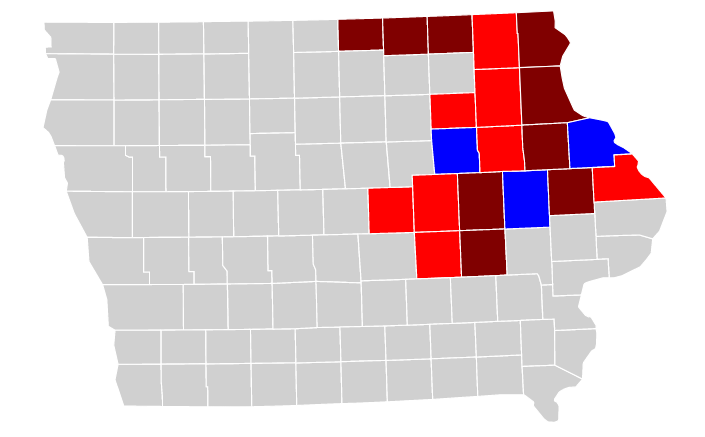
Bad faith is insidious because people are by definition not honest about what they are doing and why they are doing it. Dishonesty is corrosive, to relationships and to democracy. For example, Iowa Republicans have just passed a voter suppression bill without admitting why they did it.